Super User
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur
LIVE THIS WEEKEND - The Dream of a Generation!
This weekend, a historic and generational gathering is taking place on the National Mall in Washington D.C and we want you to join us online.
COMMUNION AMERICA: 50 TENTS, 50 STATES, ONE TABLE.
From October 10-12, believers from across the nation will come together to worship, pray, and lift high the name of Jesus over America. This is a sacred call to the Table of the Lord, a moment to plead the blood of Jesus, cry out for an end to the bloodshed, and contend for a sweeping revival in our land.
There is something powerful that happens when a generation cries out to God for a nation, and we want you to be part of it. Throughout this weekend, the Mall will be filled with the sound of worship and intercession. 50 tents representing every state, day and night, united in one heart and one cry: Jesus, heal our nation.
This is not just another event. It’s an invitation to encounter the presence of God and stand together for His purposes in our generation.
Location: Online - Download the GODTV+ app or join us at www.watch.god.tv
Friday 10th October - 11:45pm UK (BST) 6:45pm US (EST)
Saturday 11th October - 7:15pm UK (BST) 2:15pm US (EST)
Sunday 12th October - 2pm UK (BST) 9am US (EST)
Admission: Free and open to all
Let’s gather as one family, one nation, and one Church under the banner of Jesus Christ.
With faith and expectation
By Tom Victor
September 5th marked the U.S. and Canada Premiere of the new movie - Light of the World.
It is a beautifully hand-drawn animated film that follows Jesus’ life through the eyes of young John, powerfully sharing the Gospel message of love, hope, and salvation with children and families worldwide.
It is scheduled for release in 30 more nations before the end of 2025. The film will be translated into 500+ languages.
The film’s makers' vision is for the movie to nurture new and existing believers through free Gospel discipleship materials. A Gospel invitation and QR code are displayed on screen at the end of the film to encourage people to respond.
The IPC and 2BC families have been praying for the success of this remarkable film and for many children and adults across the world to be reached with its Gospel message.
Who is behind Light of the World?
The Salvation Poem Project has created Light of the World. Perhaps you’ve heard of them as the Salvation Poem is at the end of every Superbook episode and is available in almost 100 languages.
2BC and Shine!
 ‘Rise, shine, for your light has come, and the glory of the Lord rises upon you.’ (Isaiah 60:1)
‘Rise, shine, for your light has come, and the glory of the Lord rises upon you.’ (Isaiah 60:1)
On two occasions now, children from 20 nations have taken turns leading 24 hours of “on-line” prayer in our 2BC Prayer Room. Many others joined them “off-line” as well. They were part of the newly established Shine Project.
The vision of Shine! is to be praying for children (and adults) to know Jesus, boldly share His love, and for the Light of the World movie to impact families and nations with the Gospel. Watch the Trailer!
These Shine 24 hour events have been so successful that due to popular demand, we are holding a third one one! -
Shine! – 24 Hours of Prayer for the Light of the World’
October 14, 2025
Starts: 00:00 EST | 06:00 CEST | 12:00HRS SGT
Shine! is a 24-hour global celebration of Jesus, hosted by children, families, churches and ministries across every continent. We’re lifting up the name of Jesus and praying for the success of the upcoming “Light of the World” movie – a powerful Gospel film being translated into hundreds of languages.
Continuous online Zoom sessions and offline local gatherings will blend worship, intercession, creativity and child-led passion. Children will pray boldly, worship joyfully, and share Jesus faithfully!
You can join an hour online or lead your own gathering at home or church using our free Shine! Small Group Pack. Let’s raise a wave of worship and intercession that covers the earth - through the voices of the next generation!
Why is our 2BC Family partnering with this movie?
2BC has three core values. 1) Children Hearing the Voice of their Heavenly Father; 2) Children Knowing their Identity in Christ; 3) Children Empowered by God’s Spirit to Share His Love with Others. Light of the World is a powerful resource to help children – both the little ones and the older ones - become 2BC Champions as they discover their identity and share the message of God’s love with others in their neighborhood and around the world.
The Shine Project has created several free resources to help children Shine! as 2BC Champions in support of this movie, including a Prayer Guide, B.L.E.S.S. Cards, God’s Favorite and Shine Songs. There are some exclusive Light of the World resources launching this week too!
You can find them all at:https://www.2bc.world/shine/

Is the Shine Project for me?
You can only qualify for the Shine Project if:
- You are a child;
- You love children;
- You were a child at some time in your life.
If any of these apply, Light of the World and the Shine Project is for You!!! Check it out!
Here’s a music video by Shane and Shane with movie segments that can help you decide:
More info, Resources and Sign-up
www.2bc.world/shine
2BC: Every Child - Everywhere - On Mission - With God!
Join the Eurasia 24/7 Prayer Summit – Called to the Wall!
13-15 October 2025 (Optional Prayer Journey on 16th) - Island of Malta
Across Europe and the Middle East, there’s a rising sense of urgency and hope. The spiritual heritage of these lands runs deep, and many believe we are standing on the threshold of a great awakening.
In this pivotal hour, Jericho Walls International Prayer Network and IPC warmly invite you to the Eurasia 24/7 Prayer Summit, taking place 13–15 October 2025 on the beautiful island of Malta.
The summit’s theme, “Called to the Wall,” echoes the powerful words of Isaiah 62:6-7:
“I have set watchmen on your walls, O Jerusalem; they shall never hold their peace day or night. You who make mention of the Lord, do not keep silent, and give Him no rest till He establishes and till He makes Jerusalem a praise in the earth.”
God is raising up watchmen—men and women who will not rest until Heaven touches Earth in Western Europe, Eastern Europe, and the Middle East. The Eurasia Summit is a gathering for those who carry a burden for prayer for revival in these regions. Leaders from every nation in this vast and diverse part of the world will gather in Malta to celebrate what God is doing and contend for what is yet to come.
This summit is part of a global movement, one of five strategic gatherings around the world, all carrying the same vision: to see 24/7 prayer established in every nation on earth by 2033.
The mission is clear—to encourage, equip, and empower leaders to build unceasing prayer in local churches, cities, and nations.
Whether you are a pastor, prayer leader, intercessor, or simply someone burning with a vision to see God move in your nation, this summit is for you. Let’s unite across borders, languages, and cultures to lift up one sound, one cry, one relentless prayer: “God, have Your way in our nations!”
Watch the video: https://youtu.be/C1_y6nitYfg
Join us in Malta this October. Let’s answer the call to the wall—together!
Links to all IPC Projects:
https://linktr.ee/ipcprayer
Light of the World Movie
www.lightoftheworld.com/
110 Cities Prayer
www.110cities.com | Daily Prayer Fuel Sign Up
Global Family 24-7 Prayer Room
www.globalfamily24-7prayer.org/
Prayer Covenant for Children Mobile App
theprayercovenant.org/mobileapp/
Pentecost Global Day of Prayer Replays
VIEW AND WATCH ON YOUTUBE HERE
Interseed House of Prayer App
prod.global.interseed.io/link/groups?id=146
Shine! – All age prayers for the ‘Light of the World’ movie – 14th Oct 2025
https://www.2bc.world/shine
Communion America Oct 9-12th
awakenthedawn.com/communionamerica/
15 Days of Prayer for the Hindu World
12-26 October 2025
www.110cities.com
Eurasia Prayer Summit – 13-15 October 2025
jwipn.com/eurasia-24-7-prayer-summit-2025/
Global Day of Prayer for the Hindu World
20th October 2025 – From 8am (EST)
www.110cities.com
Forests in the Seed: How Kingdom Movements are Multiplying Across the Unreached World
by William J. Dubois (Author), Stan Parks (Author), Justin Long (Author)
Forests in the Seed opens a window into the 21st century of God's plan to multiply His Kingdom to everyone everywhere.
Rather than a theory-based "how-to" book, this is a testimony of what is happening now as men, women, and children raised to new life in Christ are denying themselves, taking up their cross, and following Him. The stories within this book are remarkable, supernatural in nature, and yet also lay out simple principles of multiplication found in Scripture.
Perhaps most incredible is a pattern weaved together of everyday people compelled by a vision of a resurrected Christ, who are being used in extraordinary ways to spread the Gospel in nearly impossible places. There is a spiritual revolution underway, and Forests in the Seed is your invitation to join and help change the world.
Publisher: Patmos Education Group (September 29, 2024)
Every week, Seed Co invites you to join us in praying toward ZERO, the day when not a single person is left without Scripture in their language.
This week’s journal brings you stories of God’s Word reaching hearts in the Americas:
- We pray for healing for 2 translation workers in Mexico.
- A project to translate the Chachi New Testament has come to life.
- Adilton shares his story of 20 years of commitment to bible translation and church planting.
- Praise report from the ‘Bible for All Peoples’ 2nd Conference in Brazil.
As you read, you will also find specific daily prayer points from global updates to personal stories of faith that guide you in praying strategically with others.
What a joy it is to witness God’s work and to join other believers in prayer. Thank you for standing in the gap until all people have access to Scripture.
Read, Pray, Join Us on this Assignment!
Blessings,
The Pray For Zero Family

Foundations for the Foundation is a powerful and timely book written to help everyday followers of Jesus understand God's heart for unity between Jewish and Gentile believers.
Rooted in Jesus’ prayer for oneness in John 17, this short but deep book highlights vital biblical truths that have often been lost or misunderstood throughout Church history.
The book explains how Jesus (Yeshua in Hebrew) came first to the Jewish people and how the early Church was birthed by Jewish believers. Over time, however, the Church became mostly Gentile and distanced itself from its Jewish roots. This separation has led to division and even centuries of misunderstanding and mistreatment of the Jewish people by Christians.
Now, as more Jewish people are coming to faith in Jesus than ever before, God is inviting His Church to heal this historic rift.
This restoration is not about going back to the Old Testament law but reconnecting with the full story of the Gospel—one that includes both Israel and the Nations.
The authors describe this as forming “One New Family” or “One New Man” (Ephesians 2), where Jews and Gentiles stand side by side, united in faith, purpose, and love.
Each chapter, written by respected Christian and Messianic leaders, explores different aspects of this reconnection - from understanding God’s covenant with Israel, to embracing our shared calling in the Great Commission, to learning how united prayer plays a vital role in God’s end-time purposes.
The book also emphasizes the need for love, humility, and repentance, especially from Gentile believers, to rebuild trust and partnership with Jewish believers.
Written in a clear, humble, and Spirit-led tone, Foundations for the Foundation isn’t about theology alone - it’s a call to action. It invites believers to return to God’s heart, align with His purposes, and take their place in a global move of reconciliation and revival.
Whether you are new to faith or a long-time believer, this book will open your eyes to the “Israel piece” in God’s redemptive plan and help you walk in greater love, unity, and spiritual power as the Body of Christ prepares for the return of the King.
The book is available as a print pdf / e-pub format for FREE - HERE
It will be available as a paperback book in the fall
Years ago, I was taught how to pray the Word of God - and it has revolutionized my prayer life. It is the ultimate prayer manual written by God Himself.
Scripture is the language of God’s heart!
The Bible always makes His will clear to us through the written Word. Anything the Holy Spirit makes known to us will always agree with God’s revealed Word.
As 2 Timothy 3:16-17 writes, God has always been looking for those to whom he can speak, those who will hear and live.
The Word of God isn’t casual, and it isn’t an option; our very lives depend on it!
As Jesus declared in the wilderness, “Man does not live by bread alone but by every word that proceeds out of his mouth” (Matthew 4:4). One of the ways that we learn to listen and talk to God is through Praying His Word!
It is about the rediscovery of hearing, delighting in, trembling before, and obeying the Word of God. The Word is meant to abide in us and transform us from the inside out! God’s Word feeds us (Matt. 4:4), washes us (Eph. 5:26-27), sanctifies us (John 17:17), disciplines us (Heb.4:12-13), imparts faith to us (Rom. 10:17), and equips us (2 Tim. 3:16-17).
May we get into the Word until the Word gets into us, both the written Word and the Living Word, the Lord Jesus!
At its core, prayer is the conversational part of the most essential love relationship in our lives! Prayer is intimacy with God, knowing God, and being known by God that leads to the fulfilment of his purposes. His power accomplishes it, which is all for His Glory and our Joy!
One of the practical ways that God invites us to ‘keep company with him’ is through praying Scripture. Hebrews 4:12 states that the Word of God is alive and powerful, or living and active! Along with reading God’s Word and studying God’s Word, we want to meditate on God’s Word – as Psalm 1 says,
“But his delight is in the law of the Lord, and on his law he meditates day and night. He is like a tree planted by streams of water, which yields its fruit in season and whose leaf does not wither. Whatever he does prospers” (Psalm 1:2-3).
Meditation on God’s Word and His Ways, or simply put, Praying God’s Word, is how the Spirit of God writes the Word of God on the hearts of the people of God. Something about meditation allows God’s truth to trickle from our heads to our hearts and through our hearts to our lives!
This booklet is simply a tool to help you spend time with God in his Word!
DOWNLOAD PRAY the WORD for FREE (PDF)
I encourage you to pray the Scriptures out loud, turning truth into personal dialogue with the Lord. My hope is that you will experience more and more of his life, his love, and his power!
For the Supremacy of Christ in all things,
Dr. Jason Hubbard - Director
International Prayer Connect
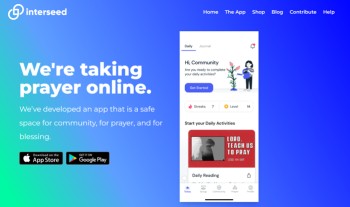
Join the Online Global Prayer Movement with the Interseed App
Imagine thousands of believers from every nation, tribe, and tongue united in prayer—lifting their voices day and night before the throne of God. With the Interseed Online House of Prayer app, this vision is becoming a reality.
Developed to mobilise united, Scripture-led prayer for the nations, Interseed is more than just an app—it’s a growing global prayer family.
Whether you're on a lunch break, commuting, or awake in the night, you can log in and instantly join with other followers of Jesus to intercede for cities, nations, unreached people groups, and urgent needs.
At the heart of the app is the Prayer Wall—a live feed where believers post real-time prayer requests and praise reports. You can respond with a tap, adding your voice to prayers already rising like incense before the Lord (Revelation 5:8). Every “amen” is a vote of faith in God's power to move.
You’ll also find daily prayer points, themed prayer rooms, and video devotionals from prayer leaders worldwide. Whether you're passionate about revival, mission, justice, healing, or the next generation, there’s a space for you to engage and grow in your calling as an intercessor.
Dr. Jason Hubbard, Director of International Prayer Connect, says:
"We’re witnessing a new era of global, united prayer—Interseed is helping us connect and pray as one Body across time zones and cultures."
We invite you to download the app, create a free account, and take your place in this extraordinary, end-time movement of prayer.
- Post your own prayer requests
- Pray for others and mark them as prayed for
- Join virtual prayer rooms focused on strategic regions
- Receive real-time notifications for urgent global needs
- Be strengthened and encouraged through community prayer
Let’s fill the airwaves with prayer.L
et’s believe for awakening, revival, and the fulfilment of the Great Commission in our day.
Download the Interseed app today on iOS or Android
Visit https://interseed.io to learn more
Together, let’s build a canopy of prayer across the nations - until the earth is filled with the knowledge of the glory of the Lord!